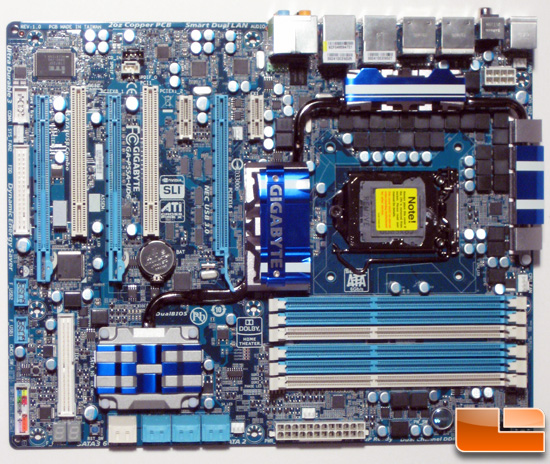
Papan induk (Inggris: motherboard) adalah papan sirkuit tempat berbagai komponen elektronik saling terhubung seperti pada PC atau Macintosh dan biasa disingkat dengan kata mobo.
Pengertian lain dari Motherboard atau dengan kata lain mainboard adalah papan utama berupa pcb yang memiliki chip bios (program penggerak), jalur-jalur dan konektor sebagai penghubung akses masing-masing perangkat.
Motherboard yang banyak ditemui dipasaran saat ini adalah motherboard milik PC yang pertama kali dibuat dengan dasar agar dapat sesuai dengan spesifikasi PC IBM. Motherboard atau disebut juga dengan Papan Induk Motherboard merupakan komponen utama dari sebuah PC, karena pada Motherboard-lah semua komponen PC anda akan disatukan. Bentuk motherboard seperti sebuah papan sirkuit elektronik. Motherboard merupakan tempat berlalu lalangnya data. Motherboard menghubungkan semua peralatan komputer dan membuatnya bekerja sama sehingga komputer berjalan dengan lancar.
Komponen-komponen Papan induk (motherboard)
Konektor power adalah pin yang menyambungkan motherboard dengan power supply di casing sebuah komputer. Pada motherboard tipe AT, casing yang dibutuhkan adalah tipe AT juga. Konektor power tipe AT terdiri dari dua bagian, di mana dua kabel dari power supply akan menancap di situ. Pada tipe ATX, kabel power supply menyatu dalam satu header yang utuh, sehingga Anda tinggal menancapkannya di motherboard. Kabel ini terdiri dari dua kolom sesuai dengan pin di motherboard yang terdiri atas dua larik pin juga. Ada beberapa motherboard yang menyediakan dua tipe konektor power, AT dan ATX. Kebanyakan motherboard terbaru sudah bertipe ATX.
- Socket atau Slot Prosesor
Terdapat beberapa tipe colokan untuk menancapkan prosesor Anda. Model paling lama adalah ZIF ( Zero Insertion Force) Socket 7 atau popular dengan istilah Socket 7. Socket ini kompatibel untuk prosesor bikinan Intel, AMD, atau Cyrix. Biasanya digunakan untuk prosesor model lama (sampai dengan generasi 233 MHz). Ada lagi socket yang dinamakan Socket 370. Socket ini mirip dengan Socket 7 tetapi jumlah pinnya sesuai dengan namanya, 370 biji. Socket ini kompatibel untuk prosesor bikinan Intel. Sementara AMD menamai sendiri socketnya dengan istilah Socket A, di mana jumlah pinnya juga berbeda dengan socket 370. Istilah A digunakan AMD untuk menunjuk merek prosesor Athlon. Untuk keluarga prosesor Intel Pentium II dan III, slot yang digunakan disebut dengan Slot 1, sementara motherboard yang menunjang prosesor AMD menggunakan Slot A untuk jenis slot yang seperti itu.
VIA VT8751A yang memberikan interface prsessor dengan frekuensi 533/400MHz, yang mensupport intel Hypertheading Tecnologi, interface system memory yang beropersi pada 266MHz, dan interface AGP 1.5V yang mendukung spesifikasi AGP 2.0 termasuk write protocol dengan kecepatan 4X.
Juga ada dua tipe socket memori yang kini beredar di masyarakat komputer. Memang ada juga socket terbaru untuk Rambus-DRAM tetapi sampai kini belum banyak pengguna yang memakainya. Socket lama yang masih cukup populer adalah SIMM. Socket ini terdiri dari 72 pin modul. Socket yang kedua memiliki 168 pin modul, yang dirancang satu arah. Anda tidak mungkin memasangnya terbalik, karena galur di motherboard sudah disesuaikan dengan socket memori tipe DIMM.
Konektor ini menghubungkan motherboard dengan piranti simpan computer seperti floppy disk atau harddisk. Konektor IDE dalam sebuah motherboard biasanya terdiri dari dua, satu adalah primary IDE dan yang lain adalah secondary IDE. Konektor Primary IDE menghubungkan motherboard dengan primary master drive dan piranti secondary master. Sementara, konektor secondary IDE biasanya disambungkan dengan pirantipiranti untuk slave seperti CDROM dan harddisk slave. Bagaimana menyambungkan pin dengan kabel? Mudah sekali. Pita kabel IDE memiliki tanda strip merah pada salah satu sisinya. Strip merah tersebut menandai, sisi kabel berstrip merah ditancapkan pada pin bernomor 1 di konektornya. Bila menancap terbalik, piranti yang terpasang tidak akan dikenali oleh komputer. Hal yang sama berlaku untuk menyambungkan kabel floppy dengan pin di motherboard.
Slot port penyelerasi gambar ini mensupport grafik card mode 3.3V/1.5V AGP 4X untuk aplikasi grafis 3D.
Peripheral kontroler terintegrasi VIA VT8235 yang mensupport berbagai I/O fungsi termasuk 2-channel ATA/133 bus master IDE controller, sampai 6 port USB 2.0, interface LCP super I/O, interface AC’97 dan PCI 2.2.
Led ini menyala jika terdapat standby power di motherboard. LED ini bertindak sebagai reminder (pengingat) untuk mematikan system power sebelum menghidupkan atau mematikan mesin.
Pegembangan slot PCI 2.2 32-bit in9i mensopport bus master PCI cart seperti SCSI atau cart LAN dengan keluaran maksimum 133MB/s.
Konektor hijau 6 pin ini adalah untuk mouse.
Pada tipe AT, port serial dan paralel tidak menyatu dalam satu motherboard tetapi disambungkan melalui kabel. Jadi, di motherboard tersedia pin untuk menancapkan kabel. Fungsi port paralel bermacammacam, mulai dari menyambungkan komputer dengan printer, scanner, sampai dengan menghubungkan komputer dengan periferal tertentu yang dirancang menggunakan koneksi port paralel. Port serial biasanya digunakan untuk menyambungkan dengan kabel modem atau mouse. Ada juga piranti lain yang bisa dicolokkan ke port serial. Dalam motherboard tipe ATX, port paralel dan serial sudah terintegrasi dalam motherboard, sehingga Anda tidak perlu menancapkan kabel-kabel yang merepotkan.
Port 25-pin ini menghubungkan konektor LAN melalui sebuah pusat network.
Jack line in (biru muda) menghuungkan ke tape player atau sumber audio lainnya. Pada mode 6-channel, funsi jack ini menjadai bass/tengah.
jack line out (lime) ini menghubungkan ke headphone atau speaker. Pada mode 6-channel, funsi jack ini menjadi speaker out depan.
Jack mic (pink) ini meghubungkan ke mikrofon. Pada mode 6-channel funsi jack ini rear speaker out belakang.
- USB 2.0 port 1 dan port 2
Kedudukan port USB (universal serial bus) 4-pin ini disediakan untuk menghubungkan dengan perangkat USB 2.0.
- USB 2.0 port 3 dan port 4
Kedudukan port USB (universal serial bus) 4-pin ini disediakan untuk menghubungkan dengan perangkat USB 2.0.
- Video Graphics Adapter Port
Port 15-pin ini adalah untuk VGA monitor atau VGA perangkat lain yang kompatibel
Ada dua tipe konektor yang menghubungkan motherboard dengan keyboard. Satu adalah konektor serial, sedangkan satu lagi adalah konektor PS/2. Konektor serial atau tipe AT berbentuk bulat, lebih besar dari yang model PS/2 punya, dengan lubang pin sebanyak 5 buah. Sementara, konektor PS/2 memiliki lubang pin 6 buah dan diameternya lebih kecil separuhnya dibanding model AT.
Batere ini berfungsi untuk memberi tenaga pada motherboard dalam mengenali konfigurasi yang terpasang, ketika ia tidak/belum mendapatkan daya dari power supply